Game Framework的两种实现方式
一年多前,曾经写过一篇关于Game Engine Framework的文章,当时基本上是为了巩固并加深对framework的理解。最近又做了一些关于framework的工作,对于framework的实现方式又有了些新的认识。虽然我现在做的已经完全不是game了,不过方式对于game也同样适用。
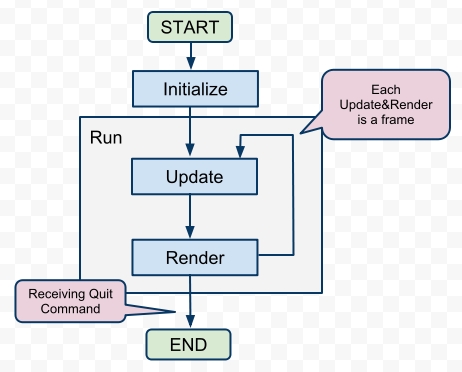
这篇文章主要希望通过一些示例性的C++代码介绍game framework的两种实现方式。首先,我还是搬出一年多前的那篇文章里的game流程图,以下的一些代码也主要基于这张图实现。对于图的细节在这里不再赘述,可以再去翻看之前的那篇文章。
1.通过继承
这是一种最传统的方式了,之前我一直使用这种方式。基本上是提供一个基类,基类封装并决定了整个程序控制流,同时基于该控制流,基类提供了一系列的接口(在C++里是虚函数),以供继承类override,并实现定制化的行为。就像下面的这个Game类,run函数决定了整个程序的执行逻辑,同时initialize,update,render等非纯虚函数则提供了接口以供用户定制并实现具体Game想要的行为。
// 通过继承来实现的framework
class Game
{
public:
void run()
{
m_isQuit = false;
initialize();
while ( !m_isQuit )
{
handleInput();
update();
render();
}
destroy();
}
protected:
virtual void initialize() {}
virtual void update() {}
virtual void render() {}
virtual void destroy() {}
virtual void onMouse( Mouse mouse ) {}
virtual void onKeyboard( Keyboard keyboard ) {}
private:
void handleInput()
{
Event e;
while ( popEvent( &e ) )
{
switch ( e.type )
{
case EVENT_QUIT:
m_isQuit = true;
break;
case EVENT_MOUSE;
onMouse( e.mouse );
break;
case EVENT_KEYBOARD:
onKeyboard( e.keyboard );
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
private:
bool m_isQuit;
};
在上面的代码中,我把实现全部写在了类的定义头文件中,在这里只是为了省事,在现实中你最好还是分开在.h和.cpp文件中。而且在这里,Game类还可以做的更多,我这里只是为了说明实现方式,所以依照前面的流程图而尽量让它简单。另外,不要纠结这段代码中的Event,Mouse,Keyboard等几个类和popEvent方法,它们只是我为了将故事说得更圆满一点而假象出来的几个类,我想你应该能猜到它们是用来干嘛的。
基于此framework,一个具体的游戏只需要重写这些虚函数就可以了,像下面的这些代码。
class ConcreteGame : public Game
{
private:
void initialize()
{
// do some real initialization
}
void update()
{
// do some real update
}
void render()
{
// do some real rendering
}
void destroy()
{
// do some real destroy
}
void onMouse( Mouse mouse )
{
// handle mouse event
}
void onKeyboard( Keyboard keyboard )
{
// handle keyboard event
}
};
int main()
{
ConcreteGame mygame;
mygame.run();
return 0;
}
2.通过Delegation模式
前一种方法有一个缺点,就是将程序的控制流和具体行为紧耦合在了一起,而且还必须使用继承,不易于扩展。现代软件设计的一些方法告诉我们,要尽量使用接口,且尽量使用组合而非继承。Delegation模式就可以帮我们达到这一目的。
何为Delegation模式,wiki上的解释一语中的:
Delegation is the simple yet powerful concept of handing a task over to another part of the program.
Delegation将一些task委托给程序的另外一部分来处理,以达到了行为使用者和具体行为的松耦合。
以下是通过Delegation模式重新实现的framework。
// 通过Delegation模式来实现的framework
class GameDelegation
{
public:
virtual void initialize() {}
virtual void update() {}
virtual void render() {}
virtual void destroy() {}
virtual void onMouse( Mouse mouse ) {}
virtual void onKeyboard( Keyboard keyboard ) {}
};
class Game
{
public:
Game( GameDelegation *gameDelegation )
{
m_gameDelegation = gameDelegation;
}
void run()
{
m_isQuit = false;
if ( m_gameDelegation == NULL )
{
return;
}
m_gameDelegation->initialize();
while ( !m_isQuit )
{
handleInput();
m_gameDelegation->update();
m_gameDelegation->render();
}
}
private:
void handleInput()
{
Event e;
while ( popEvent( &e ) )
{
switch ( e.type )
{
case EVENT_QUIT:
m_isQuit = true;
break;
case EVENT_MOUSE;
m_gameDelegation->onMouse( e.mouse );
break;
case EVENT_KEYBOARD:
m_gameDelegation->onKeyboard( e.keyboard );
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
private:
bool m_isQuit;
GameDelegation *m_gameDelegation;
};
基于此framework,当需要具体实现一个游戏的时候,只需要实现GameDelegation接口即可,然后将Game类的GameDelegation设置为你所实现的具体的ConcreteGameDelegation类,代码如下。
class ConcreteGameDelegation : public GameDelegation
{
public:
void initialize()
{
// do some real initialization
}
void update()
{
// do some real update
}
void render()
{
// do some real rendering
}
void destroy()
{
// do some real destroy
}
void onMouse( Mouse mouse )
{
// handle mouse event
}
void onKeyboard( Keyboard keyboard )
{
// handle keyboard event
}
};
int main()
{
ConcreteGameDelegation myGameDelegation;
Game mygame( &myGameDelegation );
mygame.run();
return 0;
}
最近我正好做了一些iOS上开发的研究,发现Delegation在iOS框架中被普遍使用。比如,iOS中的每个应用程序对应的是一个UIApplication类,为每一个UIApplication,开发人员必须要实现一个特定的UIApplicationDelegate,并将它指定给当前的应用程序(在main函数中通过UIApplicationMain函数指定,或者是在nib文件中绑定)。在这个UIApplicationDelegate类中,开发人员就需要重写诸如didFinishLaunchingWithOptions,applicationWillTerminate这样的方法,就类似与上面game framework中的initialize,destroy等方法。当然iOS框架要复杂很多,它还用到其它一系列的设计模式,有空研究些这样设计是非常有趣的。

图片来自于这篇苹果官方关于iOS中delegation的介绍:http://developer.apple.com/library/ios/#documentation/General/Conceptual/DevPedia-CocoaCore/Delegation.html